Quality MR imaging for Diagnosing Prostate Cancer - DxTx Medical
DxTx medical device products help radiologists and urologists with enhanced imaging offering additional treatment options for the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.
Endorectal coil, prostate image quality, prostate scans, prostate MRI, MRI images, prostate images, prostate cancer, prostate cancer treatment, prostate cancer diagnosis, increase prostate image quality, increase signal to noise, radiologists, urologists.
17768
page-template,page-template-full_width,page-template-full_width-php,page,page-id-17768,page-child,parent-pageid-16354,theme-bridge,bridge-core-3.0.9,qi-blocks-1.3.1,qodef-gutenberg--no-touch,woocommerce-no-js,qodef-qi--no-touch,qi-addons-for-elementor-1.7.6,qode-page-transition-enabled,ajax_fade,page_not_loaded,,columns-4,qode-child-theme-ver-1.0.0,qode-theme-ver-30.6.1,qode-theme-bridge,qode_header_in_grid,wpb-js-composer js-comp-ver-7.8,vc_responsive,elementor-default,elementor-kit-17954
Quality MR imaging for Diagnosing Prostate Cancer
Home > News > Quality MR imaging for Diagnosing Prostate Cancer
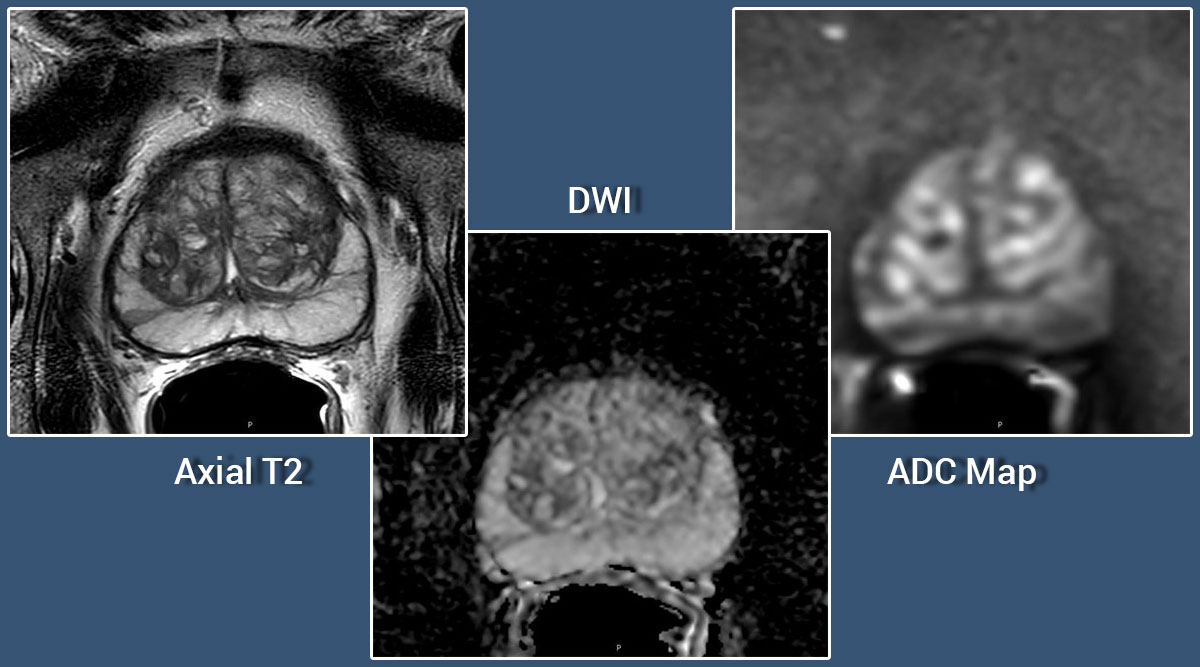
Importance of Quality MR imaging for Diagnosing Prostate Cancer
When a patient presents with elevated prostate-specific antigen and/or an abnormal digital rectal examination, the common next step in the work up for prostate cancer is a core needle biopsy under transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) guidance. Prostate cancer is not always reliably visualized with ultrasound, so the TRUS is primarily used to direct the needle into various anatomic regions of the prostate.
Sextant biopsy techniques have been shown to miss up to 50% of small tumors (1). This has led to the more widespread adoption of “saturation biopsy” techniques where 8 to 22 cores are obtained in a single biopsy session focusing on the transition zone or using a perineal template. However, lack of suitable tools to locate cancer within the prostate means that, even with saturation biopsy protocols, initial biopsy may fail to reveal cancers in up to 30% of men (2).
Multi-parametric MRI has become the standard for prostate imaging to assist in the detection, localization and staging of cancerous lesions. These imaging techniques have significantly improved the ability to identify areas of suspicion and to determine if advanced cancers have penetrated beyond the prostatic capsule.
Using MRI before an invasive procedure to identify and characterize suspicious areas can help reduce the need for first and repeat biopsies and possibly help limit the number of core samples taken during a biopsy. If the need for biopsy is established then MRI imaging fused with TRUS facilitates a targeted, non-random biopsy approach.
Bearing in mind the incidence of prostate cancer (approx. 270,000 in the US) and the number of annual prostate biopsies (approx. 1 million performed as first or repeat biopsies in roughly 70,0000 men in the US), there is a clear need for enhanced imaging to help accurate diagnosis and to reduce unnecessary procedures and cost.
Many imaging centers use the eCoil with its demonstrated image quality for prostate imaging in order to increase diagnostic confidence. Why not consider applying the DxTx Medical eCoil in your prostate imaging practice to enhance your diagnostic ability, avoid potential complications of invasive procedures, and improve the quality of care for your patients?
1.Levy DA, Jones JS. Management of rising prostate-specific antigen after a negative biopsy. Curr Urol Rep 2011;12:197–202.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
2.Ukimura O, Coleman JA, de la Taille A, Emberton M, Epstein JI, Freedland SJ, et al. Contemporary role of systematic prostate biopsies: indications, techniques, and implications for patient care. Eur Urol 2013;63:214–30.CrossRefPubMedGoogle Scholar
CONTACT INFORMATION
Contact us to to fast track your account set up.
Email: [email protected]
Phone: 1-833-777-DXTX (3989)
Interested in finding out more about our products?